Table of Contents
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of cosmetics and commodities, the design and planning of a laboratory are crucial for ensuring product quality, compliance, and innovation. This case study explores the laboratory planning and design process for a prominent cosmetic and commodities manufacturer from Kenya.
Specializing in products such as cream shampoo, lotion, hand soap, shower gel, and toilet soap, the customer is not only focused on the Kenyan market but also aims to expand globally, including into the UAE. Their choice to work with us underscores the importance of professional, high-quality lab furniture and expert planning in achieving their ambitious goals.
Understanding the Customer’s Needs
The Kenyan manufacturer approached us with a clear vision for their laboratory. Their objective was to create a state-of-the-art facility that would support their diverse product range and global expansion. They needed more than just functional lab furniture; they required a comprehensive planning approach that ensured their laboratory was equipped to handle rigorous testing, formulation, and quality control processes.
The customer emphasized their need for the best quality products and professional guidance, which is why they chose us—our reputation as a specialized lab furniture manufacturer made us the ideal partner for this project.
Key Considerations in Laboratory Planning and Design
Customized Lab Furniture Solutions
Functional Design: We focused on providing customized lab furniture that met the specific needs of the customer’s various lab rooms. From formulation benches to quality control stations, each piece was designed to enhance workflow and efficiency.
Durability and Safety: Given the chemical nature of the products, durability and safety were paramount. Our furniture was crafted from high-quality materials to withstand the demands of a busy cosmetic lab while ensuring a safe working environment.
Optimizing Laboratory Layout
Efficient Workflow: The lab was designed with an emphasis on efficient workflow, minimizing unnecessary movement and streamlining processes. Each area, from formulation to testing, was strategically planned to support smooth operations.
Zoning for Different Functions: Distinct zones were created for specific functions such as formulation, testing, and quality control. This zoning helps maintain focus and prevents cross-contamination, crucial for producing high-quality cosmetic products.
Global Compliance and Standards
Regulatory Compliance: With a global vision, it was essential that the laboratory design complied with international standards. We ensured that the facility met both Kenyan and UAE regulatory requirements, including safety standards and quality control protocols.
Documentation and Record Keeping: Adequate facilities for documentation and record-keeping were incorporated to support regulatory compliance and provide a clear audit trail.
Advanced Testing Equipment: The lab was equipped with the latest technology for testing and analysis, ensuring accurate results and reliable data. This includes advanced instruments for measuring product stability, ingredient concentration, and safety.
Integration of New Technologies: We incorporated flexible design elements to accommodate future technological advancements, ensuring the lab remains cutting-edge as the industry evolves.
The Value We Brought
The customer chose us not only for our high-quality lab furniture but also for our professional expertise in laboratory design and planning. Our ability to create a tailored solution that added significant value to their operations was a key factor in their decision. By integrating our knowledge of lab furniture with their specific needs, we delivered a facility that supports their current production and future growth ambitions.
The Detailed Planning and Design For The Laboratory
QC CHANGE ROOM
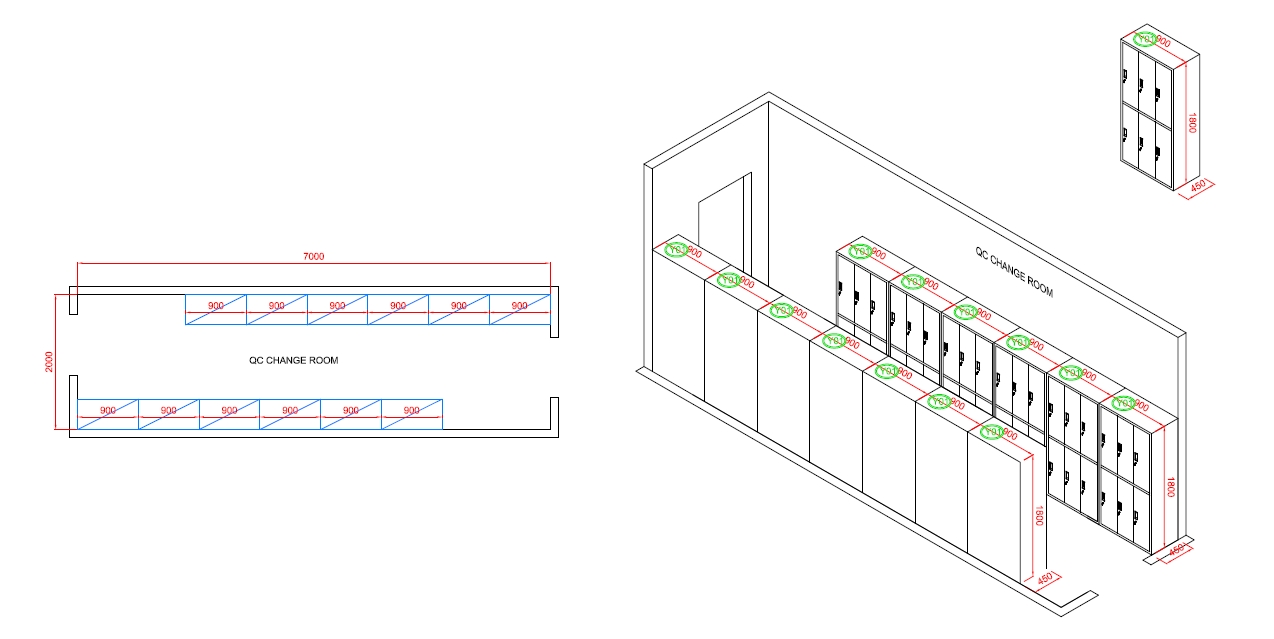
The Function Of The QC Change Room
A QC (Quality Control) change room in a cosmetic factory laboratory serves several critical functions to ensure the safety, cleanliness, and integrity of the products being tested and produced. Here’s a breakdown of its primary functions:
Contamination Control: The QC change room acts as a buffer zone between the external environment and the clean areas of the laboratory. Workers change from their street clothes into lab-specific attire to minimize the introduction of contaminants such as dust, microbes, and other foreign particles.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Storage: The change room is equipped with storage for PPE, including lab coats, gloves, hairnets, and masks. This ensures that all personnel have access to and are wearing the necessary protective gear before entering the laboratory.
Hygiene Maintenance: Workers often wash their hands and sanitize before entering the lab from the change room. This step is crucial in maintaining hygiene standards, especially in a cosmetic factory where product purity is paramount.
Segregation of Work Zones: The change room helps segregate different work zones within the laboratory, reducing the risk of cross-contamination between different areas, such as the production area and the QC laboratory.
Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Many regulatory bodies, such as the FDA or GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices), require that cosmetic manufacturing facilities maintain strict cleanliness and contamination control standards. A QC change room helps meet these regulatory requirements.
R&D AREA
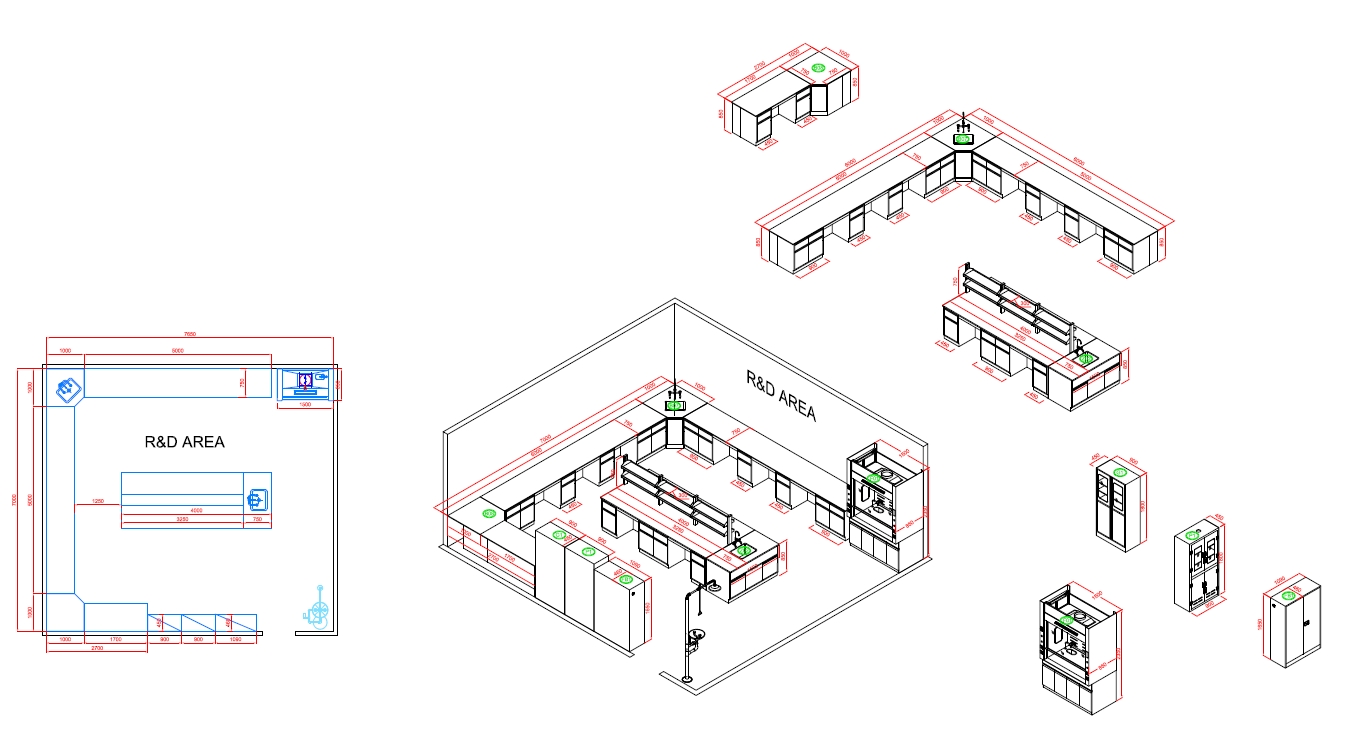
The Function Of R&D Area
The R&D (Research and Development) area in a cosmetic factory laboratory is crucial for innovation, product development, and the improvement of existing products. Here’s an overview of its key functions:
New Product Development: The primary function of the R&D area is to develop new cosmetic products. Scientists and researchers experiment with various ingredients, formulations, and techniques to create innovative products that meet consumer needs and market trends.
Formulation and Testing: In the R&D lab, formulations are designed, tested, and refined. This includes developing the right balance of active ingredients, preservatives, fragrances, and colors to achieve the desired product performance, stability, and sensory attributes.
Ingredient Research: The R&D team investigates and evaluates new raw materials, ensuring they are safe, effective, and compliant with regulatory standards. This research is essential for creating products that offer unique benefits or improvements over existing products.
Prototyping and Sampling: The R&D area is where prototypes of new products are created. These samples are used for internal testing, consumer trials, and feedback collection, which helps refine the final product before full-scale production.
Performance and Stability Testing: Products developed in the R&D area undergo rigorous performance testing to ensure they meet the intended claims, such as long-lasting effects or moisturizing properties. Stability testing is also conducted to verify that the product remains effective and safe under various storage conditions over time.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Assessments: The R&D team ensures that all products comply with local and international regulations. This includes conducting safety assessments, reviewing ingredient lists, and ensuring proper labeling.
Improvement of Existing Products: The R&D area also focuses on enhancing existing products by improving formulations, increasing efficiency, or incorporating new technologies and trends.
Collaboration with Marketing and Production: R&D works closely with the marketing department to align product development with market demands and trends. They also collaborate with the production team to ensure that new formulations can be scaled up efficiently and cost-effectively.
MICRO TESTING ROOM
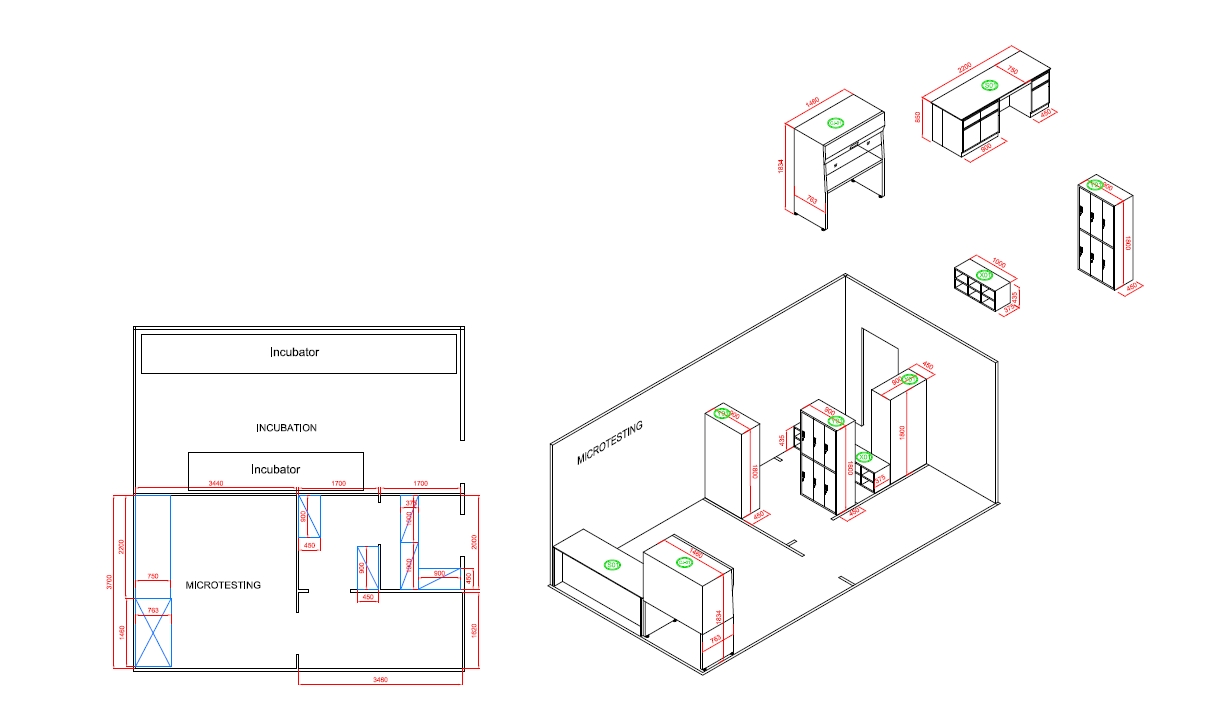
The Function Of Micro Testing Room
The microbiological (micro) testing area in a cosmetic factory laboratory is critical for ensuring the safety, quality, and stability of cosmetic products by detecting and controlling microbial contamination. Here are the primary functions of this area:
Microbial Contamination Detection: The micro testing lab conducts tests to detect the presence of harmful microorganisms, such as bacteria, yeast, and molds, in raw materials, finished products, and production environments. This ensures that products are free from contaminants that could harm consumers.
Quality Assurance: Micro testing is a key part of quality assurance, ensuring that products meet safety standards and regulatory requirements. By verifying that products are microbiologically safe, the lab helps maintain the overall quality and reputation of the cosmetic brand.
Preservative Efficacy Testing (PET): The lab assesses the effectiveness of preservatives used in cosmetic products. This testing ensures that preservatives can adequately prevent microbial growth throughout the product’s shelf life, even after opening.
Environmental Monitoring: The micro testing lab monitors the production environment, including air, water, surfaces, and equipment, to detect any potential sources of contamination. This helps maintain a clean and controlled production environment, reducing the risk of product contamination.
Sterility Testing: For products that must be sterile, such as those used in sensitive areas like the eyes or on broken skin, the micro testing lab performs sterility tests to ensure that no viable microorganisms are present.
Routine Product Testing: Regular testing of batches during production ensures consistency and safety. This includes testing samples from different production stages to ensure that microbial contamination is controlled at every step.
Investigating Microbial Failures: If a product fails micro testing, the lab investigates the source of contamination and provides insights into how to address the issue. This may involve reviewing raw materials, manufacturing processes, or storage conditions.
Regulatory Compliance: Micro testing ensures that cosmetic products comply with local and international microbiological standards and regulations, such as those set by the FDA or European Commission. This is essential for the product’s legal marketability.
Media Preparation and Storage Area
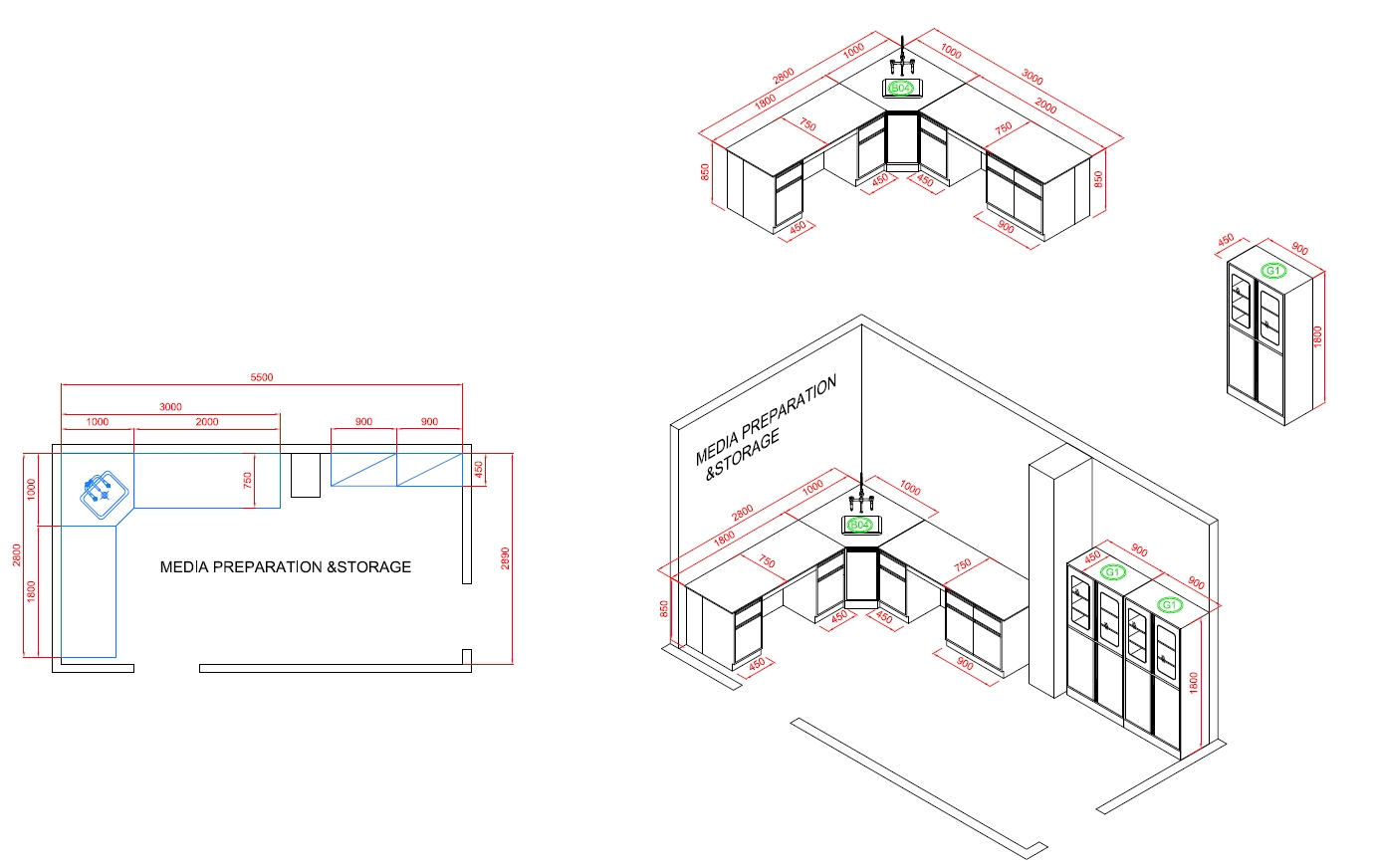
The Function Of The Media Preparation and Storage
The media preparation and storage area in a cosmetic factory laboratory is essential for supporting various microbiological testing processes. This area is responsible for the preparation, sterilization, and storage of the culture media used in testing. Here’s an overview of its key functions:
Preparation of Culture Media: The primary function is to prepare culture media, which are substances that support the growth of microorganisms. These media are critical for performing microbiological tests, such as detecting contamination in cosmetic products, raw materials, and the production environment.
Sterilization: After preparation, the culture media are sterilized to eliminate any existing microorganisms that could interfere with testing results. Sterilization is usually done using an autoclave, which uses high pressure and temperature to ensure the media are free from contaminants.
Quality Control of Media: Before use, the prepared media are often subjected to quality control tests to verify their effectiveness in supporting microbial growth. This ensures the reliability and accuracy of microbiological tests conducted in the laboratory.
Storage of Prepared Media: Once prepared and sterilized, the culture media are stored under controlled conditions to maintain their integrity until needed for testing. Proper storage conditions, such as temperature and humidity, are crucial to prevent degradation and contamination of the media.
Inventory Management: The media preparation and storage area is also responsible for managing the inventory of raw materials used to make culture media, as well as the prepared media itself. This involves tracking expiration dates and ensuring that an adequate supply is available to meet the laboratory’s needs.
Support for Microbiological Testing: The culture media prepared and stored in this area are used for various microbiological tests, such as total viable count (TVC), sterility testing, preservative efficacy testing, and environmental monitoring. These tests are essential for ensuring the microbiological safety of cosmetic products.
Standardization and Consistency: The media preparation area ensures that all culture media are prepared consistently according to standardized protocols. This standardization is crucial for obtaining reliable and reproducible results in microbiological testing.
Documentation Room
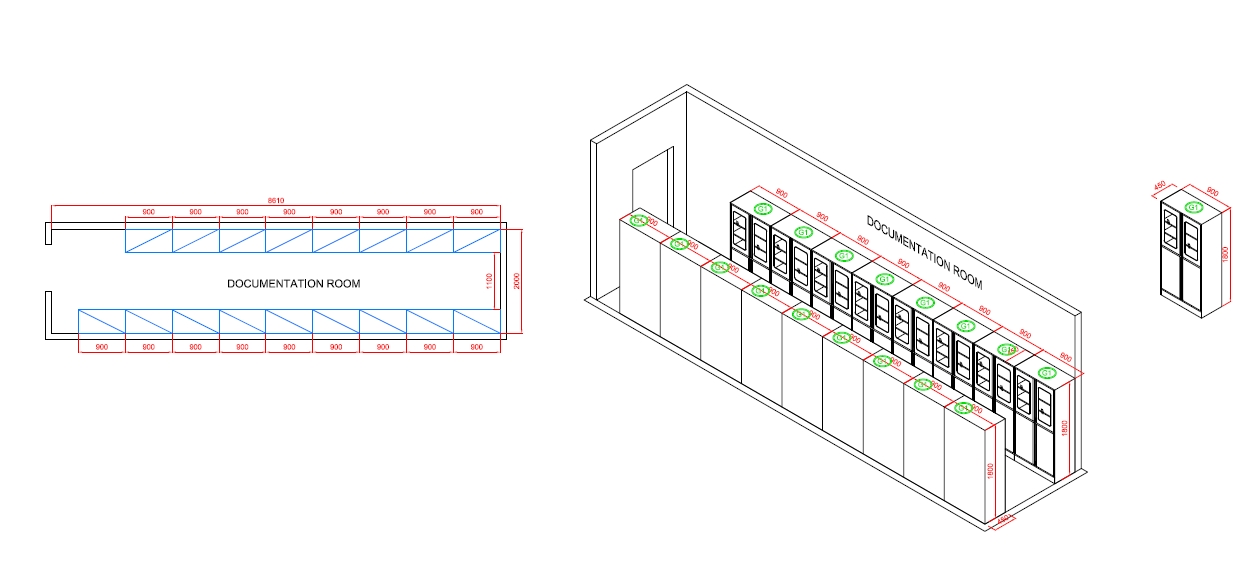
The Fuction Of Documentation Rom
The documentation room in a cosmetic factory serves as a centralized location for managing, storing, and maintaining all critical documents related to the manufacturing process, quality control, regulatory compliance, and overall operations. Here are the key functions of a documentation room:
Centralized Document Storage: The documentation room provides secure and organized storage for all essential documents, including standard operating procedures (SOPs), batch records, quality control reports, testing protocols, and regulatory filings. This ensures that all documentation is easily accessible when needed.
Regulatory Compliance: Proper documentation is crucial for compliance with local and international regulations governing cosmetic manufacturing, such as those from the FDA, EU, or other regulatory bodies. The documentation room ensures that all records are up-to-date and readily available for audits, inspections, or regulatory reviews.
Quality Control and Assurance: The documentation room houses records of quality control processes, test results, and quality assurance activities. This allows for easy traceability and verification of product quality, ensuring that manufacturing practices meet the required standards.
Batch Record Management: Detailed batch records are maintained to document the production of each batch of cosmetic products. These records include information on raw materials, production processes, and testing outcomes. In the event of a product recall or investigation, batch records are crucial for identifying affected products.
SOPs and Work Instructions: The documentation room stores all standard operating procedures and work instructions that guide the manufacturing process. These documents ensure that all employees follow consistent, standardized practices, which is essential for maintaining product quality and safety.
Change Control Documentation: Any changes to processes, equipment, or formulations are documented through a formal change control process. The documentation room keeps records of these changes, including approvals and justifications, to ensure that all modifications are properly evaluated and implemented.
Record Retention and Archiving: The documentation room manages the retention and archiving of records according to legal and regulatory requirements. This includes maintaining documents for the required duration and securely disposing of them when they are no longer needed.
Confidentiality and Security: Sensitive information, such as proprietary formulations, ingredient specifications, and intellectual property, is stored securely in the documentation room. Access to these documents is often restricted to authorized personnel to protect the company’s confidential information.
Audit Preparation and Support: During internal or external audits, the documentation room provides easy access to required records and documentation. Well-organized documentation is critical for demonstrating compliance and ensuring successful audit outcomes.
Training Records Management: The documentation room may also store training records for employees, ensuring that all personnel have received the necessary training for their roles. This is important for both regulatory compliance and maintaining a skilled workforce.
Stability Chamber
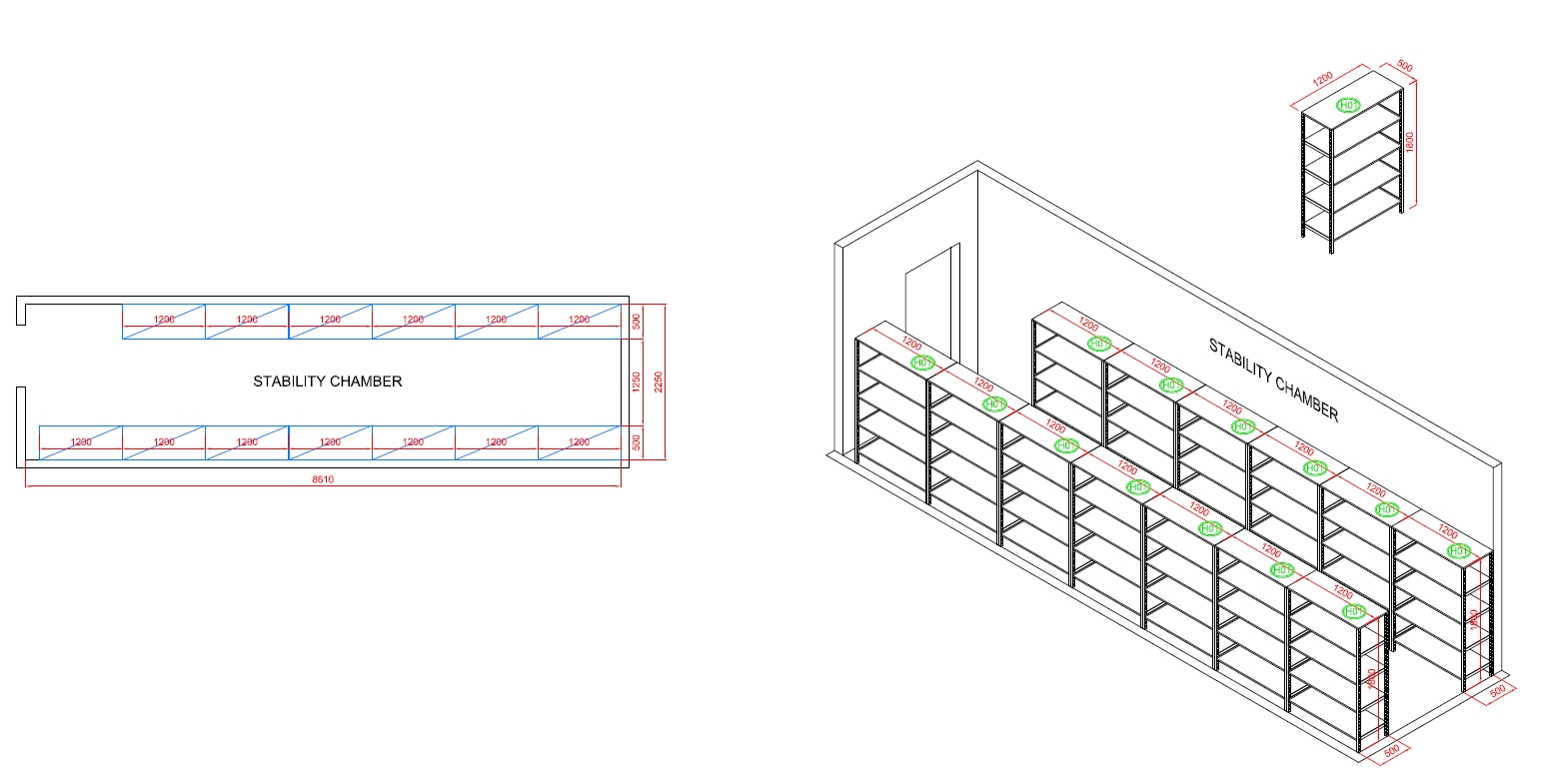
The Function Of Stability Chamber
The stability chamber in a cosmetic factory is a controlled environment used to test and assess the stability of cosmetic products over time. Its main purpose is to ensure that products maintain their quality, safety, and efficacy throughout their intended shelf life. Here are the key functions of a stability chamber:
Environmental Simulation: The stability chamber simulates various environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure, that a cosmetic product might encounter during storage and use. This helps predict how the product will behave under different conditions.
Shelf Life Determination: By storing products in the stability chamber for extended periods, the factory can determine the product’s shelf life. This includes assessing whether the product maintains its intended characteristics, such as texture, color, fragrance, and effectiveness, without degrading over time.
Accelerated Stability Testing: The stability chamber is often used for accelerated stability testing, where products are exposed to elevated temperatures and humidity levels to speed up the aging process. This allows manufacturers to quickly gather data on how the product will perform over its shelf life.
Real-Time Stability Testing: In addition to accelerated testing, the chamber is used for real-time stability testing, where products are stored under normal conditions for the full duration of their intended shelf life. This provides a more accurate picture of how the product will perform in real-world scenarios.
Regulatory Compliance: Stability testing is a regulatory requirement in many regions, ensuring that cosmetic products meet safety and quality standards throughout their shelf life. Data from the stability chamber helps demonstrate compliance with these regulations.
Quality Control: Stability chambers are an integral part of the quality control process, ensuring that each batch of product remains consistent in quality over time. This helps identify any potential issues with formulations or packaging that could affect product stability.
Packaging Evaluation: The stability chamber also assesses the interaction between the product and its packaging. This includes checking for any adverse reactions, such as leaching of materials from the packaging into the product or changes in packaging integrity under different conditions.
Product Development Support: During product development, stability chambers are used to test new formulations and ingredients. This helps identify any stability issues early in the development process, allowing for adjustments before the product is finalized.
Troubleshooting and Improvement: If stability issues are identified, the data from the stability chamber can help pinpoint the cause, whether it’s related to formulation, packaging, or storage conditions. This information is essential for making necessary improvements to the product.
Instrument Room
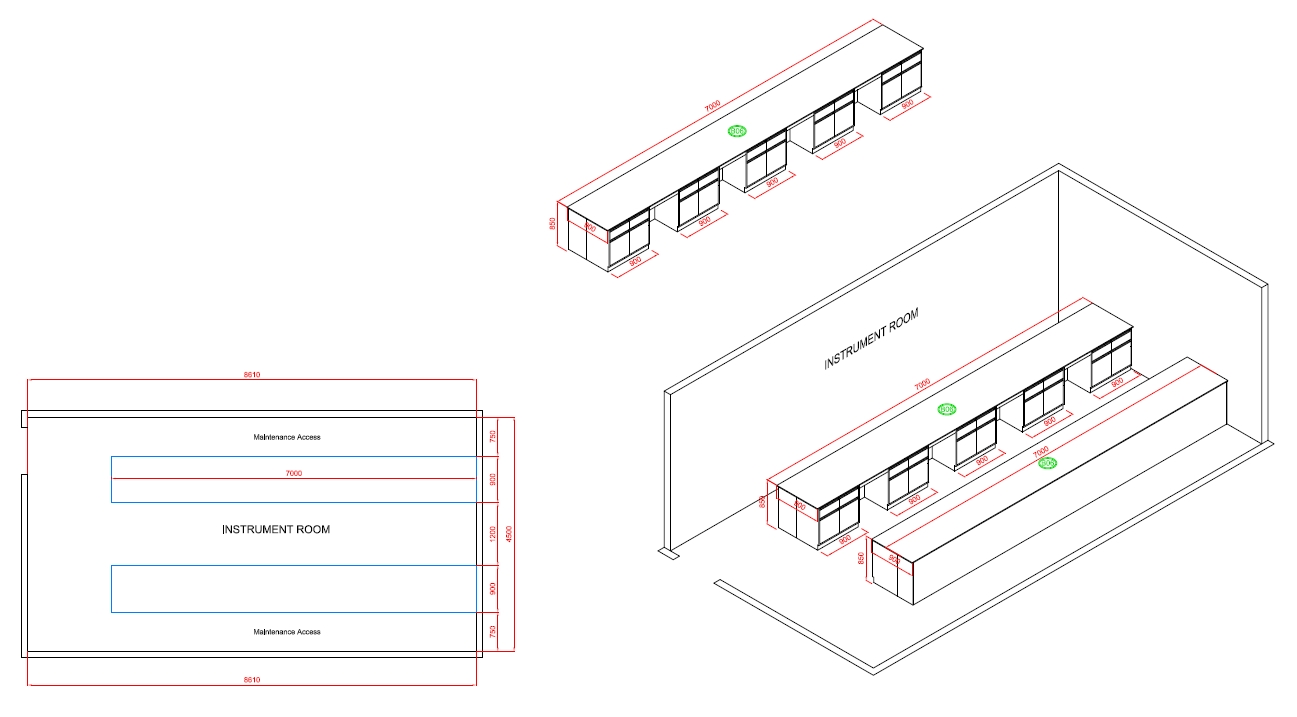
The Function Of Instrument Room
The instrument room in a cosmetic factory is a dedicated space where specialized equipment and instruments are housed, maintained, and used for various analytical, testing, and measurement purposes. It plays a crucial role in ensuring product quality, consistency, and compliance with industry standards. Here are the key functions of an instrument room:
Analytical Testing: The instrument room is equipped with advanced analytical instruments used for testing the chemical composition, purity, and concentration of raw materials, intermediate products, and finished cosmetic products. This ensures that the formulations meet specified standards and are free from contaminants.
Quality Control: Instruments in this room are used to perform precise measurements and analyses to verify that products meet quality specifications. This includes testing parameters such as pH levels, viscosity, particle size, and other critical attributes that affect product performance.
Research and Development Support: During the product development phase, the instrument room provides essential data that helps researchers and formulators optimize formulations, select appropriate ingredients, and ensure that new products will perform as intended.
Regulatory Compliance: The instrument room supports regulatory compliance by providing accurate data for documentation and reporting. This is particularly important for ensuring that products comply with safety regulations and industry standards.
Calibration and Maintenance: The instrument room is responsible for the calibration and maintenance of all analytical instruments. Regular calibration ensures that instruments provide accurate and reliable results, while maintenance helps prevent equipment malfunctions and extends the lifespan of the instruments.
Microbiological Testing: Some instruments in the room may be dedicated to microbiological testing, such as detecting microbial contamination in products. This is crucial for ensuring the microbiological safety of cosmetic products.
Physical Testing: The instrument room may also house equipment for physical testing, such as texture analyzers, colorimeters, and rheometers, which measure the physical properties of products like texture, color, and flow behavior.
Training and Education: The instrument room serves as a training area where laboratory personnel are trained to operate and maintain sophisticated instruments. Proper training ensures that staff can use the equipment effectively and accurately interpret the results.
Data Management: The data generated by the instruments in this room are critical for making informed decisions about product quality, formulation adjustments, and process improvements. The room may include computer systems for managing and analyzing this data.
Support for Troubleshooting: When issues arise during production or with product quality, the instrument room provides the tools and data necessary for troubleshooting. This helps identify the root cause of problems and enables corrective actions to be taken.
Chemical Testing And Storage Room
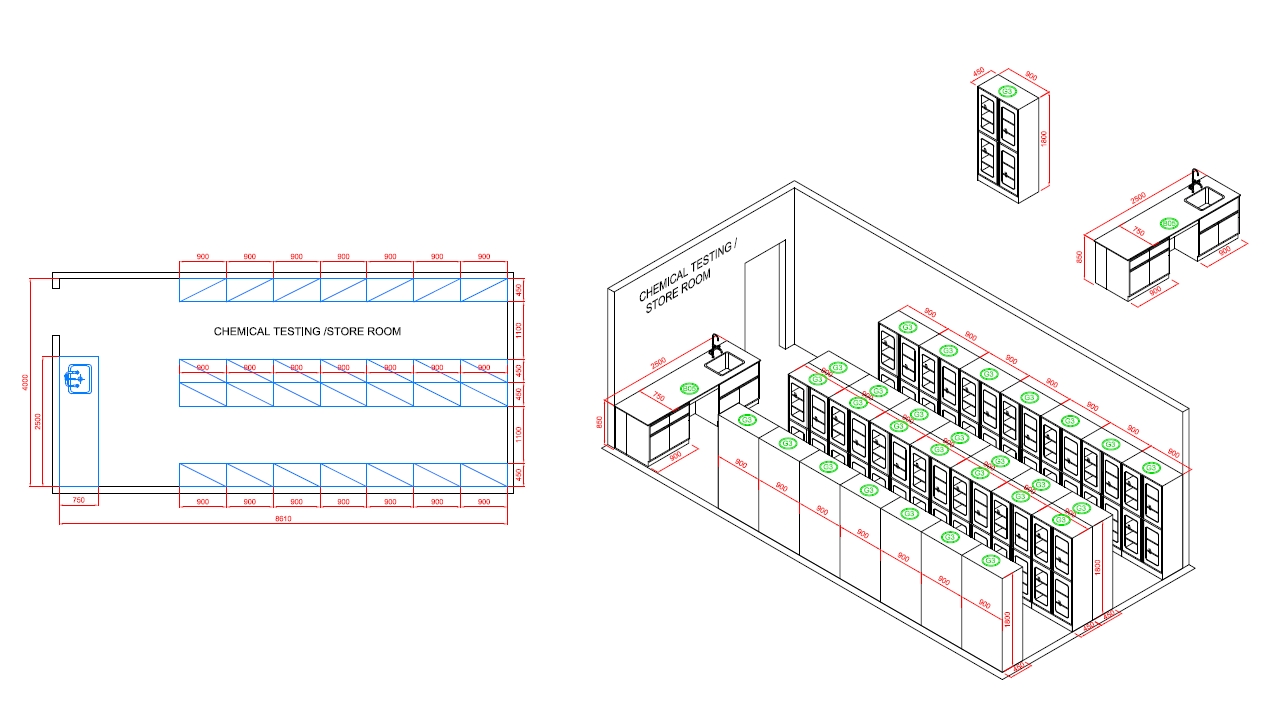
The Function Of Chemical Testing And Storage Room
The chemical testing and storage room in a cosmetic factory serves two primary functions: performing chemical analyses and safely storing chemicals used in various processes. These functions are crucial for maintaining product quality, safety, and compliance with regulatory standards. Here’s a detailed overview:
Chemical Testing
- Quality Control: The chemical testing room is equipped to conduct a variety of tests on raw materials, intermediate products, and finished cosmetic products. These tests are essential for verifying that the chemical composition of the products meets the specified standards.
- Purity and Concentration Analysis: This room is used to determine the purity and concentration of active ingredients and other chemical components in cosmetic formulations. It ensures that products are effective and safe for consumer use.
- pH Testing: The pH of cosmetic products is critical for skin compatibility and stability. The chemical testing room is where pH measurements are taken to ensure that the products fall within the desired range.
- Stability Testing: Chemical stability tests are conducted to ensure that the product remains chemically stable over time and under various environmental conditions. This helps in predicting the shelf life of the product.
- Compatibility Testing: The room is also used for compatibility testing between different ingredients, ensuring that they do not react adversely with each other, which could affect the product’s safety and performance.
- Regulatory Compliance: The chemical testing room supports regulatory compliance by providing accurate data required for documentation and reporting to regulatory authorities. This ensures that the products meet legal standards for safety and efficacy.
Chemical Storage
- Safe Storage of Chemicals: The storage room is designed to safely store chemicals used in manufacturing and testing processes. This includes raw materials, solvents, reagents, and any other chemicals necessary for production and analysis.
- Hazardous Materials Management: The storage room follows strict protocols for storing hazardous materials, such as flammable, toxic, or reactive chemicals. Proper storage minimizes the risk of accidents, spills, or chemical reactions.
- Inventory Management: The room is responsible for managing the inventory of chemicals, ensuring that there is an adequate supply for ongoing production and testing needs. It also tracks expiration dates and ensures that chemicals are used within their shelf life.
- Labeling and Documentation: Chemicals in the storage room are properly labeled and documented to ensure easy identification, compliance with safety regulations, and traceability in case of audits or inspections.
- Waste Disposal: The room may include provisions for the temporary storage of chemical waste until it can be safely disposed of according to environmental and safety regulations.
- Environmental Control: The chemical storage area is typically equipped with environmental controls, such as temperature and humidity regulation, to preserve the integrity of the stored chemicals and prevent degradation.
Safety and Compliance
- Emergency Preparedness: The chemical storage room is often equipped with safety features such as fire suppression systems, ventilation, spill containment kits, and emergency eyewash stations to handle accidents or emergencies.
- Training and SOPs: Personnel working in this area are trained in proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals. Standard operating procedures (SOPs) are followed to ensure safety and compliance with regulations.
Wet Chemistry Laboratory
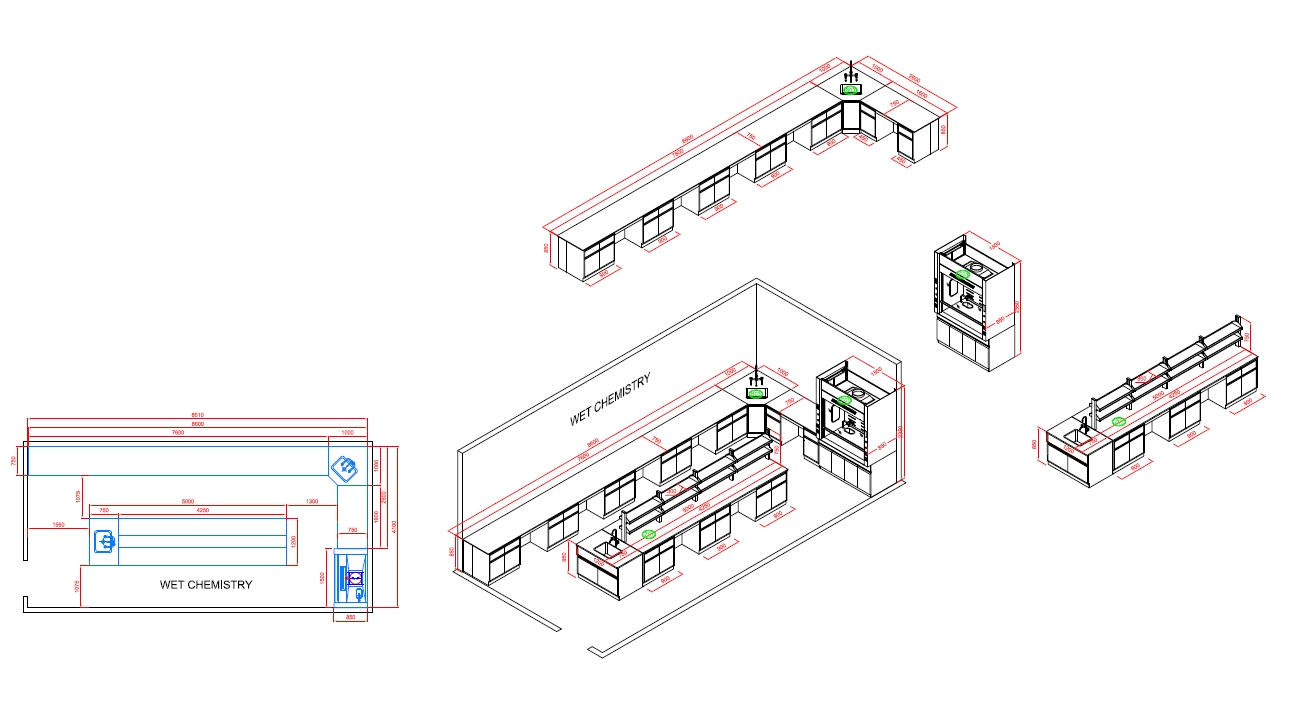
The Function Of A wet chemistry laboratory
A wet chemistry laboratory in a cosmetic factory is a specialized facility where chemical analyses involving liquid solutions and reactions are performed. This type of lab plays a crucial role in the formulation, quality control, and safety testing of cosmetic products. Here are the key functions of a wet chemistry laboratory:
Formulation Development
- Ingredient Mixing and Reaction Testing: The wet chemistry lab is used to mix and react various ingredients to develop new cosmetic formulations. This involves testing how different chemicals interact, ensuring that the final product is stable, effective, and safe.
- Solubility Testing: This lab is used to determine the solubility of various ingredients in different solvents, which is essential for creating homogenous cosmetic products like lotions, creams, and serums.
Quality Control
- Purity and Concentration Analysis: Wet chemistry techniques are employed to measure the purity and concentration of raw materials and active ingredients. Techniques such as titration, gravimetry, and colorimetry help ensure that products meet their specified chemical compositions.
- pH Measurement: One of the critical functions of the wet chemistry lab is to measure the pH levels of cosmetic products. The pH must be within a specific range to ensure the product’s safety and effectiveness on the skin.
- Contaminant Testing: The lab is also used to detect and quantify contaminants or impurities in the products, such as heavy metals or residual solvents, to ensure that they meet safety standards.
Stability Testing
- Chemical Stability: The wet chemistry lab tests the chemical stability of cosmetic products under various conditions. This involves subjecting products to different temperatures, light exposure, and humidity levels to determine how they hold up over time.
- Oxidation and Degradation Testing: Wet chemistry techniques are used to assess the potential for oxidation or degradation of ingredients, which can affect the product’s shelf life and safety.
Microbiological Support
- Preservative Efficacy Testing: The lab tests the efficacy of preservatives in the formulation by mixing them with various microbial cultures and measuring their ability to inhibit growth. This ensures that the product remains safe for use over its intended shelf life.
Regulatory Compliance
- Validation and Verification: The wet chemistry lab plays a role in validating and verifying that the manufacturing processes and end products comply with regulatory standards. Accurate documentation and testing ensure that the products meet local and international cosmetic regulations.
- Batch Testing: Before a batch of cosmetic products is released, samples are tested in the wet chemistry lab to verify that they meet the required chemical specifications, ensuring consistency across production runs.
Problem Solving and Troubleshooting
- Formulation Adjustments: If issues arise during production, such as unexpected reactions or changes in product quality, the wet chemistry lab is used to analyze the problem and make necessary adjustments to the formulation.
- Failure Analysis: The lab helps identify the causes of product failures, such as instability or separation, and provides data to guide corrective actions.
Support for R&D
- New Product Testing: The wet chemistry lab supports research and development efforts by testing new ingredients and formulations. This helps cosmetic chemists refine and perfect new products before they are scaled up for production.
- Compatibility Studies: The lab is used to conduct compatibility studies between different ingredients and packaging materials, ensuring that the final product remains stable and effective.
Wash Area
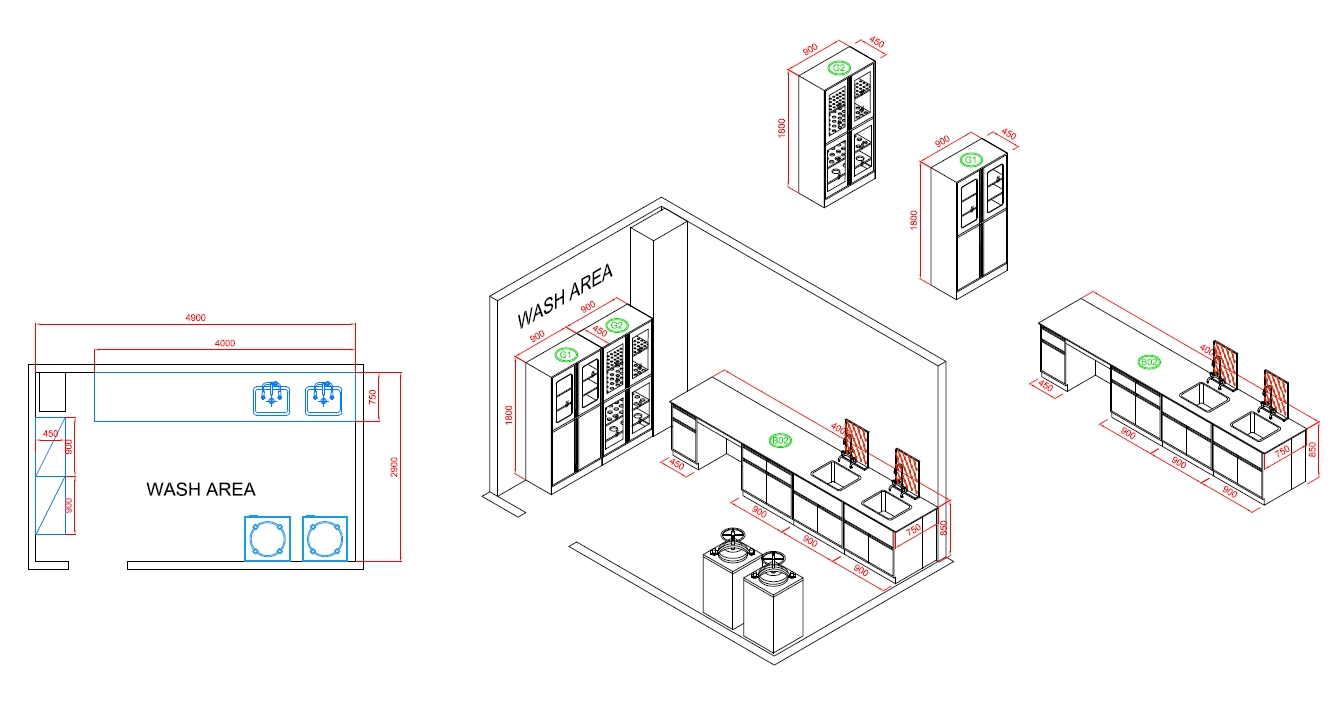
The Function Of Wash Area
A wash area in a cosmetic factory serves as a designated space for cleaning and sanitizing equipment, tools, containers, and sometimes even personnel involved in the manufacturing process. The wash area is essential for maintaining hygiene and preventing cross-contamination, which is critical in producing safe and high-quality cosmetic products. Here are the key functions of a wash area in a cosmetic factory:
Equipment Cleaning
- Sanitization of Manufacturing Equipment: The wash area is where manufacturing equipment, such as mixing vessels, filling machines, and other tools, are thoroughly cleaned and sanitized. This ensures that there is no residue from previous batches, which could contaminate new products.
- Sterilization Processes: For equipment that requires sterilization, the wash area may include facilities to perform this, ensuring that all microbial contamination is eliminated, particularly for products that are sensitive to microbial growth.
Tool and Utensil Cleaning
- Cleaning of Small Tools and Utensils: Small tools, such as spatulas, measuring devices, and other handheld instruments used during production, are cleaned in the wash area. Proper cleaning prevents any potential contamination that could affect product quality.
- Segregation of Clean and Dirty Tools: The wash area typically has designated zones or systems for segregating clean and dirty tools, helping to maintain a clear workflow and avoid cross-contamination.
Container Cleaning
- Cleaning of Reusable Containers: Reusable containers, such as drums, bottles, and other packaging materials, are cleaned and sanitized in the wash area before being filled with cosmetic products. This is crucial for maintaining product integrity and safety.
- Preparation for Next Use: After cleaning, containers are often dried and prepared in the wash area for their next use, ensuring they are in optimal condition for production.
Personnel Hygiene
- Hand and Equipment Washing: In some cases, the wash area may include facilities for workers to wash their hands or sanitize personal protective equipment (PPE) before entering sensitive production areas. This is especially important in environments where strict hygiene controls are necessary.
- Changing Areas: Some wash areas may be adjacent to changing rooms where personnel can change into clean uniforms or gowns before entering the production area, further reducing the risk of contamination.
Waste Management
- Safe Disposal of Waste Water: The wash area is equipped to handle and safely dispose of wastewater generated during cleaning activities. This includes systems to ensure that chemicals and residues are treated appropriately before being released or recycled.
- Handling Contaminated Materials: The wash area may also have protocols for handling and disposing of contaminated materials, such as rags or cleaning agents, to prevent environmental contamination and ensure compliance with waste management regulations.
Compliance and Record Keeping
- Documentation of Cleaning Procedures: The wash area often includes stations for documenting cleaning activities, ensuring that all equipment and tools are properly cleaned according to standard operating procedures (SOPs). This documentation is crucial for audits and regulatory compliance.
- Adherence to Hygiene Standards: The wash area is designed to meet specific hygiene and cleanliness standards required by regulatory bodies, ensuring that the factory maintains a clean and safe production environment.
Support for Production
- Minimizing Downtime: By having a dedicated wash area, the factory can minimize downtime between production runs, as equipment and tools can be quickly and efficiently cleaned and returned to service.
- Efficiency in Operations: The wash area helps streamline operations by providing a dedicated space where all cleaning activities are centralized, reducing the risk of contamination and improving overall workflow efficiency.
Hot Room
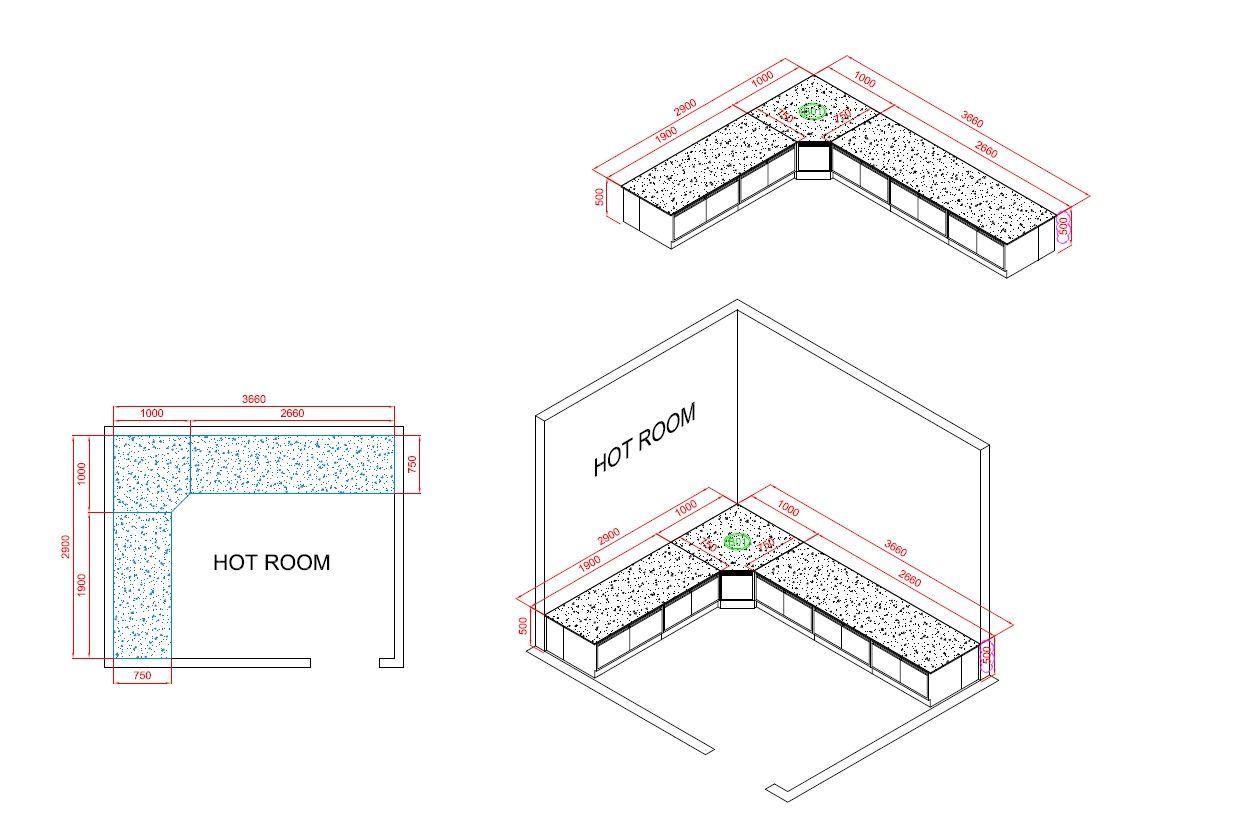
The Function Of Hot Room
The hot room in a cosmetic factory is a specialized environment designed to control and maintain elevated temperatures for various processes involved in the production of cosmetic products. Here are the key functions of a hot room:
Temperature-Controlled Processing
- Formulation and Mixing: Some cosmetic formulations require heating during the mixing process to dissolve ingredients, blend emulsions, or activate certain compounds. The hot room provides a controlled environment to maintain the necessary temperatures for these processes.
- Melting of Ingredients: Ingredients such as waxes, butters, and certain oils often need to be melted before they can be incorporated into cosmetic formulations. The hot room ensures these ingredients are melted and kept at the required temperatures.
Stability Testing
- Accelerated Stability Testing: The hot room is used for accelerated stability testing, where products are exposed to elevated temperatures to simulate long-term storage conditions in a shorter period. This helps determine how products will behave over time, including potential changes in texture, color, and efficacy.
- Heat Resistance Testing: Products and ingredients are tested for their resistance to heat to ensure they maintain their stability and performance under various temperature conditions.
Controlled Drying
- Drying of Products: Some cosmetic products, such as powders or granules, require controlled heating to ensure proper drying. The hot room provides a stable environment for drying these products without affecting their quality.
- Evaporation of Solvents: In formulations where solvents need to be evaporated, the hot room helps facilitate this process by maintaining elevated temperatures that accelerate solvent evaporation.
Batch Consistency
- Uniform Processing Conditions: The hot room ensures that all batches of product are processed under consistent temperature conditions, which is crucial for maintaining batch-to-batch consistency in product quality.
Activation of Ingredients
- Thermal Activation: Some cosmetic ingredients require heat to activate their properties or enhance their efficacy. The hot room provides the controlled temperature needed for such activation processes.
Product Testing and Quality Control
- Heat Testing: The hot room is used to test how products perform under high-temperature conditions, which helps identify any potential issues with formulation stability or product integrity.
- Quality Assurance: Regular quality checks and tests are performed in the hot room to ensure that products meet required specifications and maintain their intended properties after exposure to heat.
Compliance and Documentation
- Regulatory Compliance: The hot room helps meet regulatory requirements for certain testing and processing procedures. Proper documentation of temperature conditions and processes is maintained to demonstrate compliance with industry standards.
- Record Keeping: Detailed records of temperature settings, processing times, and test results are kept to ensure traceability and accountability.
Support for Research and Development
- Development of New Formulations: During the R&D phase, the hot room is used to develop and test new formulations that require specific temperature conditions. This helps optimize formulations and ensure they perform as intended.
If you are planning for a cosmetic & commodities laboratory, or any other type of laboratory, welcome to contact our expert in laboratory planning.




